Meet Our Doctor
Dr. Paresh Bang

Surgery For Spine Infections In Nagpur
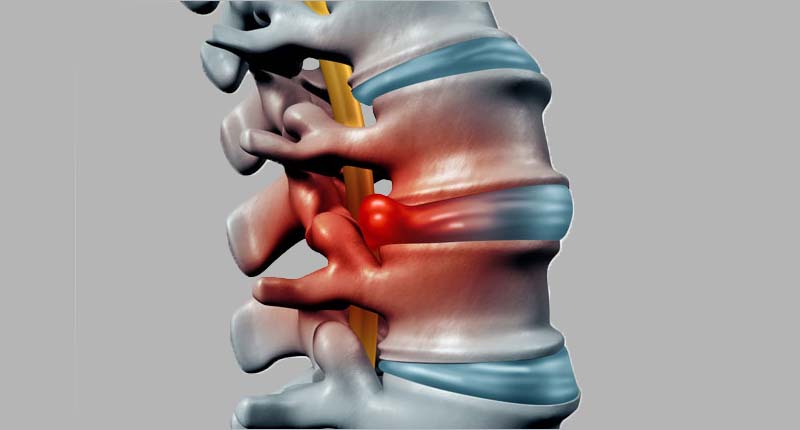
Surgery For Spine Infections
Intervertebral disc space infections involve the space between adjacent vertebrae. Disc space infections can be divided into three subcategories: adult hematogenous (spontaneous), childhood (discitis) and postoperative.
Spinal infections can be caused by either a bacterial or a fungal infection in another part of the body that has been carried into the spine through the bloodstream. The most common source of spinal infections is a bacterium called staphylococcus aureus, followed by Escherichia coli.
Spinal infections may occur after a urological procedure, because the veins in the lower spine come up through the pelvis. The most common area of the spine affected is the lumbar region. Intravenous drug abusers are more prone to infections affecting the cervical region. Recent dental procedures increase the risk of spinal infections, as bacteria that may be introduced into the bloodstream during the procedure can travel to the spine.
Symptoms vary depending on the type of spinal infection but, generally, pain is localized initially at the site of the infection. In postoperative patients, these additional symptoms may be present:
- Wound drainage
- Redness, swelling or tenderness near the incision
The biggest challenge is making an early diagnosis before serious morbidity occurs. Diagnosis typically takes an average of one month, but can take as long as six months, impeding effective and timely treatment. Many patients do not seek medical attention until their symptoms become severe or debilitating.
Nonsurgical treatment should be considered first when patients have minimal or no neurological deficits and the morbidity and mortality rate of surgical intervention is high. However, surgery may be indicated when any of the following situations are present:
Significant bone destruction causing spinal instability
- Neurological deficits
- Sepsis with clinical toxicity caused by an abscess unresponsive to antibiotics
- Failure of needle biopsy to obtain needed cultures
- Failure of intravenous antibiotics alone to eradicate the infection
